Local Network Topology Within the Various EDGE Network
Network topology is the arrangement of the elements (links, nodes, etc.) of a communication network.[12] Network topology can be used to define or describe the arrangement of various types of telecommunication networks, including command and control radio networks, [13] industrial fieldbusses and computer networks.
Network topology is the topological [14] structure of a network and may be depicted physically or logically. It is an application of graph theory [13] wherein communicating devices are modeled as nodes and the connections between the devices are modeled as links or lines between the nodes. Physical topology is the placement of the various components of a network (e.g., device location and cable installation), while Logical topology illustrates how data flows within a network. Distances between nodes, physical interconnections, transmission rates, or signal types may differ between two different networks, yet their logical topologies may be identical.
There are several different types of network topology in local area networks (LAN) and all are suitable for different purposes, depending on the overall network size and your objectives.
Ring Topology
What is it?
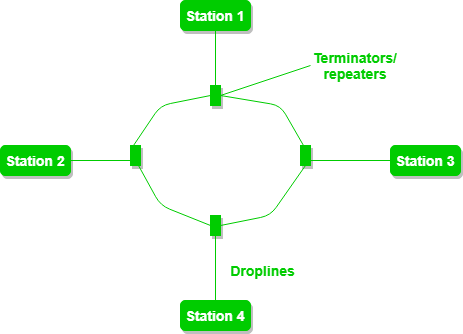
Ring topology is a type of network topology where nodes are connected in closed path to create Ring network. In a ring network, packets of data travel from one device to the next until they reach their destination. Most ring topologies allow packets to travel only in one direction, called a Unidirectional ring network. Others permit data to move in either direction, called Bidirectional.
-
Unidirectional Ring Topology
This types uses a single strong cable throughout whole Computer Network. All the Nodes are connected to this single cable. Moreover, direction of flow of data is single. It means that data can either travel in clockwise direction or in an anti-clockwise direction. -
Bidirectional Ring Topology
This type is usually more reliable but costly to build. In this type, each Network Node connects with a pair of Backbone Cable. Moreover, you can get the advantage of a Full-Duplex transmission. So, data can flow in both directions at the same time. It means that a Node can communication with two other Network Nodes at the same time.
It is used in LANs and WANs depending on the card of network in the computer.
Ring Topology Protocols
These are some simple examples of protocols. Ring Topology uses one of the following protocols:
- Token Ring
- Metro Ring Protocol
- Fiber Distributed Data Interface
Example of Ring Topology Network in Real Life

One of the common example that still exists is SONET Rings. SONET stands for Synchronous Optical Networking. It uses Fiber Optic Cables for heavy load data transfers for long distances. You can simply think SONET to be Fiber Optic Cable Ring Topology. It is highly reliable Computer Network for synchronizing various branch offices of a multi-national company. Due to the use of Fiber Optic Cable, it provides the best data transfer speeds. SONET is one of the most popular Applications of Ring Topology.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ring Topology

Bus Topology
 [4]
[4]What is it?
Bus topology is a simple design that utilizes a single length of cable, also known as the medium, with directly attached LAN stations. This topology is sometimes referred to as linear-bus topology. All stations share this cable segment. Every station on this segment sees transmissions from every other station on the cable segment; this is known as a broadcast medium. The LAN attachment stations are definite endpoints to the cable segment and are known as bus network termination points. [4]
This single cable segment lends itself to being a single point of failure. If the cable is broken, no LAN station will have connectivity or the ability to transmit and receive. Ethernet (IEEE 802.3) best represents this topology. Ethernet has the ability to utilize many different cable schemes. [4]
Instead of cable either network card, co-axial cable or RJ-47 can be used depending on the type of computers used in the network. When Bus Topology has only two endpoints, it is known as Linear Topology. In Bus topology data is transmitted only in one direction. [5]
Here, the node that transmits data is known as Host. All the computers connected in the network will receive all the network traffic. Each node is given equal priority for data transmission. The nodes use Media Access Technology such as a bus master to share the bus. [5]
Example of Bus Topology Network in Real Life
- An example of bus topology is connecting two floors through a single line.
- Ethernet networks also use a bus topology
- In a bus topology, one computer in the network works as a server and other computers behave as clients. The purpose of the * server is to exchange data between client computers.
- Printers, scanners and other input/output devices can be added in the office/home by using bus topology network. [6]
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bus Topology
Advantages
- Very simple to design.
- Require less cabling compared to other topologies.
- Each to implement for small networks.
- Easy to expand by simply joining two cables together.
- Very cost-effective.
Disadvantages
- The network stands on a single cable. So, if any damage caused to this cable the whole network falls.
- As the traffic is shared by all the nodes in the network, the performance of the network decreases as the traffic increases.
- Difficult to find the flaws and faults in the network connected with this method.
- Packet loss is high.
- This topology is very slow compared to other topologies. [5]
Star Topology

What is it?
Star topology is a type of network topology in which all the computers connect with the help of a hub. All stations are attached by cable to a central point, usually a wiring hub or other device operating in a similar function. Several different cables can be used for this point-to-point link, such as shielded twisted-pair (STP), unshielded twisted-pair (UTP), and fiber-optic cabling. Wireless media can also be used for communications links. [4]
STP cable is not typically used in a point-to-point configuration. STP is used primarily in the Token Ring environment, where the hubs are called MAUs or MSAUs and the connections from the NIC to the MAU are not really point-to-point. This is because there is a transmit and a receive side, and the transmission is one way. In fact, this is sometimes called a “star-ring,” [4] which would be a hybrid topology.
A star topology can be made by connecting bus topology. The backbone of bus topology is connected to the central hub. It is most popular on LAN networks as they are easy to install.[10]
Example of Star Topology Network in Real Life
Star topologies tend to be found in large organisations, such as educational establishments and businesses, where high performance is a must.
They are also found in home networks, especially those that are wireless. In this case, a router with a wireless access point (WAP) provides the central connection for all nodes. Ethernet network is also made by a star topology.[11]
Advantages and Disadvantages of Star Topology
Advantages
- Easy to troubleshoot, set up and modify.
- If one computer on the network fails, the rest of the network continues to function normally.
- In Star topology, addition, deletion, and moving of the devices are easy.
- Centralized management of the network, through the use of the central computer, hub, or switch.
- Easy to add, delete, and move devices to the network. [9]
Disadvantages
- The network stands on a the central hub. So, if any damage caused to this cable the whole network falls. Today, it is common to deploy hubs with built-in redundancy. Such redundancy is designed to isolate a faulty or failed component, such as the backplane or power supply. [4]
- May have a higher cost to implement, especially when using a switch or router as the central network device.
- The central network device determines the performance and number of nodes the network can handle.
- A damaged cable or lack of proper termination may bring the network down. [9]
Tree Topology
 [4]
[4]What is it?
The tree topology is a logical extension of the bus topology and could be described as multiple interconnected bus networks. The physical (cable) plant is known as a branching tree with all stations attached to it. The tree begins at the root, the pinnacle point, and expands to the network endpoints. This topology allows a network to expand dynamically with only one active data path between any two network endpoints. A tree topology network is one that does not employ loops in its topology. [4]
In tree topology, two nodes can be connected to a single parent node. The two nodes are called children of the parent node. The topology is named tree because its shape looks like a tree with different branches of nodes. The parent and child relationship in tree topology helps to search and sort a large amount of data in the network. The child nodes are also called leaves of the network. [7]
It is easy to find fault in the network and network administrator can fix the bug instantly. If any parent node gets a problem then child node stops accessing data. Tree network can be expanded easily as child nodes can become parents of future nodes. [7]
Example of Tree Topology Network in Real Life
- A bridged or switched network running the spanning tree algorithm, usually found with Ethernet (IEEE 802.3) networks. The spanning tree algorithm disables loops in what would otherwise be a looped topology. Spanning tree expands through the network and ensures that only one active path exists between any two LAN-attached stations. [4]
- Different floors can be connected to each other through combining star topology network and central bus backbone
- B-trees looks same as tree topology and it is used in different programming languages like MySQL, Redis, PostgreSQL and in filesystems including ext4, NTFS. [7]
Advantages and Disadvantages of Tree Topology
Advantages
- It is a combination of bus and star topology
- It provides high scalability, as leaf nodes can add more nodes in the hierarchical chain.
- Other nodes in a network are not affected, if one of their nodes get damaged
- It provides easy maintenance and fault identification.
- Supported by several hardware and software vendors.
- Point-to-point wiring for individual segments.
Disadvantages
- Large cabling is required as compared to star and bus topology.
- On the failure of a hub, the entire network fails.
- Tree network is very difficult to configure than other network topologies. [8]
Mesh Topology
What is it?
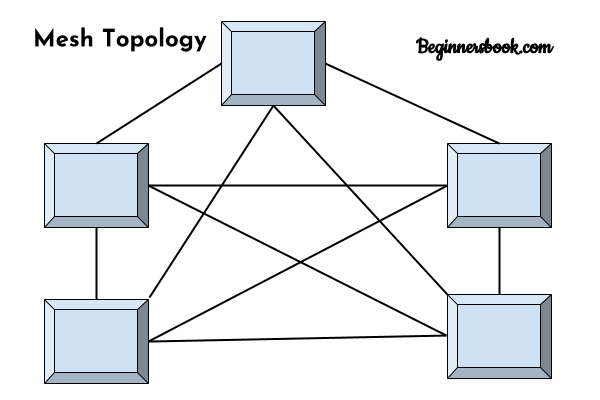
Mesh topology is a type of network topology where all nodes communicate each other. Mesh Topology Network has a high reliability and performance. in Mesh Topology the troubleshooting mechanisme is much easier than the Ring Topology but will require amount of cabling and hardware to configure your Computer Network.
In mesh topology each device is connected to every other device on the network through a dedicated point-to-point link. This means that there are dedicated links between each pair of Network Devices.
How Mesh Topology Works
Mesh Topology Work by using either Routing or Flooding mechanism. In Routing, each computer establishes a Routing Table. Every time a device wants to send information, it first looks for the communication link to receiver using routing table. Flooding involves sender to broadcast the message to all the nodes. Node having the same address as address given in the message keeps data. Otherwise, node discards the data message.
Example of Mesh Topology Network in Real Life
one of the finest Examples of Mesh Network Topology is Zigbee. Zigbee is basically a Wireless Mesh Network comprising of various types of sensors like pressure sensor, light sensor and heat sensor. It works with low power consumption devices. Moreover, devices in such a Network don`t require higher data transfer rates. Usually this type of Networks perform in a limited geographical area. So, it can be classified as Wireless Personal Area Network. the another example of it are Smart Home Control and Monitoring and Smart Agriculture Control and Monitoring.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Mesh Topology

Hybrid Topology

What is it?
Hybrid topology is a combination of two or more topologies. For example, if you combine Ring and star topology to make bigger network then it will be called hybrid network or hybrid topology. Different topologies are combined via the hubs and switches.[14]
Types of hybrid topologies
The two most commonly used types of hybrid topologies are the following.
- Star-Ring hybrid topology A star-ring hybrid topology is a combination of the star topology and ring topology. Two or more star topologies are connected together through a ring topology.[15]

- Star-Bus hybrid topology A star-bus hybrid topology is a combination of the star topology and bus topology. Two or more star topologies are connected together through a bus topology.[15] A tree network (or star-bus network) is a hybrid topology in which star networks are interconnected via bus networks. [16]

Two other hybrid network types are hybrid mesh and hierarchical star. [16]
Example of Hybrid Topology Network in Real Life

In modern network implementations, the hybrid topology is mostly used to mix the wired network with the wireless network. Unlike a wired network, a wireless network does not use cables to connect computers. A wireless network uses radio spectrum to transmit data.[17]
Hybrid topology can be found in various places, such as school, office, research organizations, banks, and automated industry. [14]
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hybrid Topology
Advantages
-
Scalable. New topologies and nodes can be added and removed from the network easily.
-
Reliable. If there occurs any error in the network then it is detected easily and that network device or node can be exchanged with a new device or node.
-
Flexible. Hybrid Network can be designed according to the requirements of the organization and by optimizing the available resources.
-
Effective. The characteristics of each topology are combined in the hybrid network and weakness of different topologies are eliminated.
Disadvantages
-
The hubs which are attached to combine different topologies are expensive. These hubs are different from normal hubs and are more intelligent in performance.
-
Designing hybrid networks is a complex process. Hybrid networks are difficult in installing and configuring.
-
If the backbone of the network is damaged then network performance is affected also.
-
A hybrid topology is used in making large networks so it needs more cables and cooling system. These types of networks also need sophisticated network devices. [14]
No network topology is perfect, or even inherently better than the others. So, determining the right structure for business will depend on the needs and the size of the network. There are key elements to consider: length of cable needed, cable type, cost and scalability.
References
- Roy, J. (2020, December 5). What is Ring Topology? Definition | Examples | Advantages | Disadvantages. Network Topology. https://topologynetwork.com/what-is-ring-topology-definition-examples-advantages-disadvantages/
- Roy, J. (2020, May 18). What is Mesh Topology? Definition: Examples: Advantages: Disadvantages. Network Topology. https://topologynetwork.com/what-is-mesh-topology-definition-examples-advantages-disadvantages/
- Hope, C. (2018, November 13). What is a Ring Topology?. https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/r/ringtopo.htm
- Castelli, M. (2002). Network Consultants Handbook. https://books.google.co.id/books?id=IR78eIcGoFcC&pg=PA20&lpg=PA20
- https://www.elprocus.com/bus-topology-in-computer-networks/
- Rehman, J. (2019). What is bus topology with example. https://www.itrelease.com/2019/06/what-is-bus-topology-with-example/
- Rehman, J. (2019). What is tree topology with example. https://www.itrelease.com/2019/06/what-is-tree-topology-with-example/
- Jahejo, A. (2019). Type of Network Topology Tree Topology | Advantages & Disadvantages of Tree Topology. https://computernetworktopology.com/tree-topology/
- Hope, C. (2018). Star Topology. https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/s/startopo.htm Retrieved 2021-2-26.
- Rehman, J. (2019). What is star topology with example. https://www.itrelease.com/2019/06/what-is-star-topology-with-example/ Retrieved 2021-2-26.
- BBC Bitesize. GCSE Computer Science: Star networks - Network topologies, protocols and layers. https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zr3yb82/revision/1 Retrieved 2021-2-26
- Groth, David; Toby Skandier (2005). Network+ Study Guide, Fourth Edition. Sybex, Inc. ISBN 0-7821-4406-3.
- Grant, T. J., ed. (2014). Network Topology in Command and Control: Advances in Information Security, Privacy, and Ethics. IGI Global. ISBN 9781466660595.
- Rehman, J. (2020). https://www.itrelease.com/2020/07/what-is-a-hybrid-topology-with-example/ Retrieved 2021-2-27.
- Hope, C. (2020). https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/h/hybrtopo.htm Retrieved 2021-2-27.
- Sosinsky, Barrie A. (2009). Networking Bible. Indianapolis: Wiley Publishing. ISBN 978-0-470-43131-3.
- ComputerNetworkingNotes. (2019). https://www.computernetworkingnotes.com/networking-tutorials/network-topologies-explained-with-examples.html Retrieved 2021-2-27.